Which of the Following Is Not a Physical Hazard Category
Physical hazard means a chemical which poses one of the following hazardous effects. Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals GHS.
They can be classified as type of occupational hazard or environmental hazard.

. These are then sub-divided into different categories depending on the degree of danger and these are assigned specific. They are used to describe 3 main types of chemical hazards. Term effects and strain longAssociated with working with animals people or infectious plant materials.
Either one or the other is chosen depending on the target. Two sets of pictograms are included within the GHS. Physical hazards are a.
Electrical hazards like frayed cords missing ground pins improper wiring or the harm that these hazards pose. So OSHA created the Hazard Not Otherwise Classified definition to cover health or physical hazards for which the standard lists a hazard class but whose effect either falls below the cut-off valueconcentration limit of the hazard class or is under a GHS hazard category that has not been adopted by OSHA. Flammable gases aerosols liquids or solids.
GHS includes criteria for the classification of health physical and environmental hazards as well as specifying. A physical hazard is an agent factor or circumstance that can cause harm with contact. Physical hazards explode ignite or react violently with other substances.
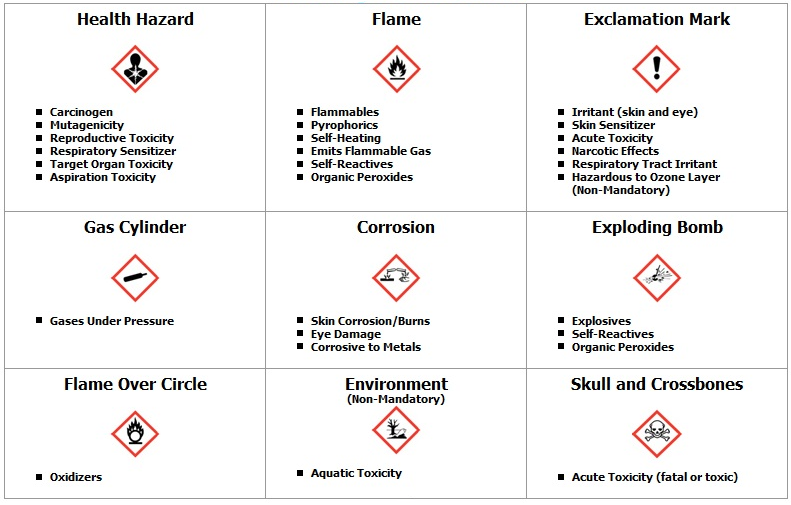
The following table lists these physical and health hazard categories that facilities have been using since 1987 to. Chemical A is Glutaraldehyde. There are five main classes of physical hazard namely Explosive Flammable Oxidising Gases under Pressure and Corrosive to metals.
Physical hazards include ergonomic hazards radiation heat and cold stress vibration hazards and noise hazards. Biological chemical physical and allergenic. GHS the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals was developed by the United Nations as a way to bring into agreement the chemical regulations and standards of different countries.
GHS Hazard Classifications Categories. For example hazard class flammable liquids can be divided into 4 categories among which flammable liquids category 1 represents the most severe hazard. Oxidizer liquid solid or gas.
There are 29 GHS hazard classes in total in UN GHS Rev. There are four primary categories of food safety hazards to consider. None of these is a physical hazard.
In contact with water emits flammable gas. Pyrophoric liquid or solid. A physical hazard is any extraneous object or foreign matter in a food item which may cause illness or injury to a person consuming the product.
Engineering controls are often used to mitigate physical hazards. Similarly what are the 4 types of food hazards. All of the chemicals listed are health hazards.
Hazard category means the division of criteria within each hazard class eg acute toxicity and flammable liquids each include four hazard categories numbered from category 1 through category 4. Harm physical injury or damage to health. 12 rows Category 1 is always the greatest level of hazard that is it is the most hazardous within that.
Physical hazards and health hazards. Physical hazards health hazards and environmental hazards. Been reporting the five consolidated hazard categories that EPA modified from OSHAs original 23 physical and health hazards.
This toolbox meeting guide gives brief descriptions of each of the 19 physical hazard classes. In WHMIS 2015 hazardous products are divided into two hazard groups. One for the labelling of containers and for workplace hazard warnings and a second for use during the transport of dangerous goods.
The HCS defines hazard class as the nature of a physical or health hazard eg flammable solid carcinogen and acute toxicity. A hazard is any source of potential damage harm or adverse health effects on something or someone. Understanding the risks associated.
A main purpose of the new GHS is to standardize the types of chemical hazards that exist and the way entities in the chemical industry classify chemicals that have those hazards. The two hazard groups are further divided into hazard classes. Short Confined spaces Machinery-related hazards lockouttagout boiler safety forklifts etc BIOLOGICAL HAZARDS.
There are many definitions for hazard but the most common definition when talking about workplace health and safety is. Prior to GHS the same chemical could be classified differently in different countries and industries resulting in confusing. Physical hazard are based on the intrinsic properties of the chemical.
These foreign objects include but are not limited to bone or bone chips metal flakes or fragments injection needles BBs or shotgun pellets pieces of product packaging stones glass or wood fragments insects or other filth. Examples of physical hazards include slips trips falls exposure to loud noises working from heights vibrations and unguarded machinery. Hazard a potential source of harm to a worker.


No comments for "Which of the Following Is Not a Physical Hazard Category"
Post a Comment